本篇文章为CoreText教程系列的第五篇,也是最后一篇。
本文实现了在纯文本排版时,监听用户的点击,并把识别到的点击内容通过NSLog打印出来。
实现的思路主要是给控件添加手势点击并进行监听,在用户点击时拿到点击的位置,并在手势识别结束后用CoreText遍历每一个CTLine,判断点击的位置是否在识别的特定字符串(比如人名或者连续的数字串)内,如果是则找出该字符串。使用CTLineGetStringIndexForPosition函数来找出点击的字符位于整个字符串的位置。
完整的代码放在了github的仓库 。
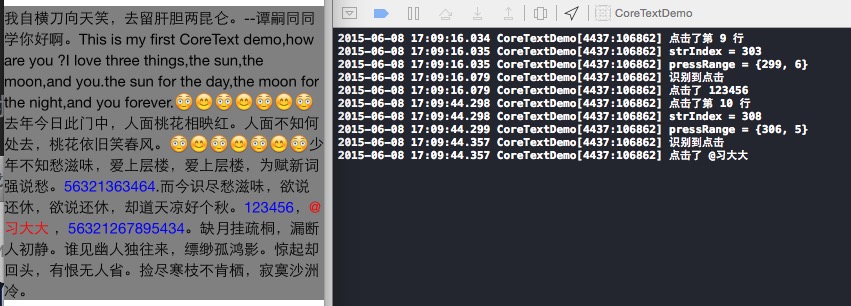
运行效果为:
大部分代码与之前一致,主要增加了使用正则表达式来检测特定的字符串,以及监听用户的点击,进行遍历找出用户点击的字符。
本文使用了正则表达式监测“@”开头空格结尾的人名和一串连续的数字。
检测的格式为:
1
2
NSString * kAtRegularExpression = @"@[^ \\ s@]+? \\ s{1}" ;
NSString * kNumberRegularExpression = @" \\ d+[^ \\ d]{1}" ;
给控件添加手势监听:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
self . longPressGesture = [[ UILongPressGestureRecognizer alloc ] initWithTarget : self action : @selector ( longPressed :)];
self . longPressGesture . minimumPressDuration = 0.01 ;
self . longPressGesture . delegate = self ;
[ self addGestureRecognizer : self . longPressGesture ];
手势识别的方法为:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
#pragma mark - 手势识别相关
- ( void ) longPressed: ( UIGestureRecognizer * ) gesture
{
if ( gesture . state == UIGestureRecognizerStateBegan )
{
} else if ( gesture . state == UIGestureRecognizerStateChanged )
{
} else if ( gesture . state == UIGestureRecognizerStateCancelled )
{
} else if ( gesture . state == UIGestureRecognizerStateEnded )
{
if ( self . pressRange . location != 0 && self . pressRange . length != 0 )
{
NSLog ( @"识别到点击" );
NSString * clickStr = [ self . text substringWithRange : self . pressRange ];
NSLog ( @"点击了 %@" , clickStr );
}
}
}
需要实现手势识别的两个代理方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
#pragma mark - UIGestureRecognizerDelegate
- ( BOOL ) gestureRecognizerShouldBegin: ( UIGestureRecognizer * ) gestureRecognizer
{
if ( gestureRecognizer == self . longPressGesture )
{
// 点击处在特定字符串内才进行识别
BOOL gestureShouldBegin = NO ;
CGPoint location = [ gestureRecognizer locationInView : self ];
CGFloat lineHeight = self . font . pointSize * kPerLineRatio ;
int lineIndex = location . y / lineHeight ;
NSLog ( @"点击了第 %d 行" , lineIndex );
// 把点击的坐标转换为CoreText坐标系下
CGPoint clickPoint = CGPointMake ( location . x , self . textHeight - location . y );
CFArrayRef lines = CTFrameGetLines ( self . ctFrame );
if ( lineIndex < CFArrayGetCount ( lines ))
{
CTLineRef clickLine = CFArrayGetValueAtIndex ( lines , lineIndex );
// 点击处的字符位于总字符串的index
CFIndex strIndex = CTLineGetStringIndexForPosition ( clickLine , clickPoint );
NSLog ( @"strIndex = %ld" , strIndex );
NSMutableAttributedString * mutableAttributed = [[ NSMutableAttributedString alloc ] initWithString : self . text ];
NSArray * checkResults = [ self recognizeSpecialStringWithAttributed : mutableAttributed ];
for ( NSValue * value in checkResults )
{
NSRange range = [ value rangeValue ];
if ( strIndex >= range . location && strIndex <= range . location + range . length )
{
self . pressRange = range ;
gestureShouldBegin = YES ;
NSLog ( @"pressRange = %@" , NSStringFromRange ( range ));
}
}
}
return gestureShouldBegin ;
}
return YES ;
}
// 该方法可实现也可不实现,取决于应用场景
- ( BOOL ) gestureRecognizer: ( UIGestureRecognizer * ) gestureRecognizer shouldRequireFailureOfGestureRecognizer: ( UIGestureRecognizer * ) otherGestureRecognizer
{
if ([ otherGestureRecognizer isKindOfClass :[ UIPanGestureRecognizer class ]])
{
return YES ; // 避免应用在UITableViewCell上时,挡住拖动tableView的手势
}
return NO ;
}
一个识别特定字符串的工具方法为:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
#pragma mark - 识别特定字符串并改其颜色,返回识别到的字符串所在的range
- ( NSMutableArray * ) recognizeSpecialStringWithAttributed: ( NSMutableAttributedString * ) attributed
{
NSMutableArray * rangeArray = [ NSMutableArray array ];
// 识别@人名
NSRegularExpression * atRegular = [ NSRegularExpression regularExpressionWithPattern : kAtRegularExpression options : NSRegularExpressionCaseInsensitive error : nil ];
NSArray * atResults = [ atRegular matchesInString : self . text options : NSMatchingWithTransparentBounds range : NSMakeRange ( 0 , self . text . length )];
for ( NSTextCheckingResult * checkResult in atResults )
{
if ( attributed )
{
[ attributed addAttribute : NSForegroundColorAttributeName value :[ UIColor redColor ] range : NSMakeRange ( checkResult . range . location , checkResult . range . length - 1 )];
}
[ rangeArray addObject :[ NSValue valueWithRange : checkResult . range ]];
}
// 识别连续的数字
NSRegularExpression * numberRegular = [ NSRegularExpression regularExpressionWithPattern : kNumberRegularExpression options : NSRegularExpressionCaseInsensitive | NSRegularExpressionUseUnixLineSeparators error : nil ];
NSArray * numberResults = [ numberRegular matchesInString : self . text options : NSMatchingWithTransparentBounds range : NSMakeRange ( 0 , self . text . length )];
for ( NSTextCheckingResult * checkResult in numberResults )
{
if ( attributed )
{
[ attributed addAttribute : NSForegroundColorAttributeName value :[ UIColor blueColor ] range : NSMakeRange ( checkResult . range . location , checkResult . range . length - 1 )];
}
[ rangeArray addObject :[ NSValue valueWithRange : NSMakeRange ( checkResult . range . location , checkResult . range . length - 1 )]];
}
return rangeArray ;
}
本次教程是我在自己学习的过程中,边学边写的。一来检查自己的学习效果,而来分享学习心得也可顺便帮助其他初学者。
CoreText学习起来并不难,只是其属于偏底层的实现,需要花费多一些的时间。